Describe What Happens During a Polymerase Chain Reaction
PGR is a three-step process or cycle. Calculate the maximum change in temperature that the reaction tube experiences during one cycle of PCR b.
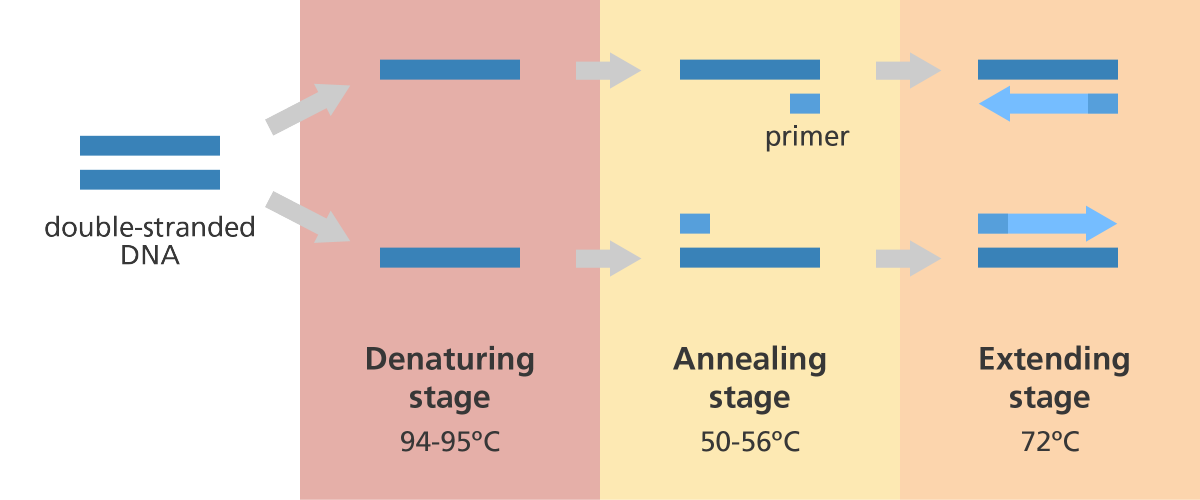
What Are The Three Basic Steps Of Conventional Pcr Praxilabs
The melding of a technique for repeated rounds of DNA synthesis with the discovery of a thermostable DNA polymerase has given scientists the very powerful technique known as polymerase chain reaction PCR.

. PCR Polymerase Chain Reaction is a revolutionary method developed by Kary Mullis in the 1980s. PCR is based on using the ability of DNA polymerase to synthesize new strand of DNA complementary to the offered template strand. PCR is the most reliable and accurate test for detecting active infection.
The polymerase chain reaction PCR is a laboratory technique for DNA replication that allows a target DNA sequence to be selectively amplified. The polymerase chain reaction is a three step cycling process consisting of defined sets of times and temperatures. During a polymerase chain reaction smaller segments of DNA are being copied.
3 basic PCR steps include. Because significant amounts of a sample of DNA are necessary for molecular and genetic analyses studies of isolated pieces of DNA are nearly impossible without PCR amplification. Polymerase chain reaction PCR is a laboratory procedure that can create replicas of DNA.
This technique was developed in 1983 by Kary Mullis an American biochemist. The Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR is a technique for the amplification of DNA in vitro this describes experiments with. Sometimes called molecular photocopying conventional polymerase chain reaction PCR is a technique used to amplify replicate trace amounts of DNA and RNA from a sample.
PCR tests typically take hours to perform but some are faster. Principle Procedure Components Types and Applications. The polymerase chain reaction PGR amplifies a single piece of DNA across several orders of magnitude see figure 62.
Once cooled the primers bind to one of the strands and the process of replicating starts with the help of the DNA polymerase. Each of these steps requires a different temperature range which allows PCR machines to control the steps. A PCR thermal cycler is used to produce the large amounts required for research.
1 denaturation of the template into single strands. The polymerase chain reaction PCR uses enzymes to mass replicate a portion of a deoxyribonucleic acid DNA strand for easier analysis such as searching for genes of interest. This is accomplished by using thermal cycling a process in which a solution that includes DNA is repeatedly heated and cooled in order to 1 melt the DNA 2 anneal short DNA fragments called primers typically artificially.
Completion of the final step and the first cycle of PCR resulting in a doubling of the amount of DNA template present. This tests for the presence of the actual viruss genetic material or its fragments as it breaks down. Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR.
PCR can use the smallest sample of the DNA to be cloned and amplify it to millions of copies in just a few hours. Is the process of polymerase chain reaction similar to the process of DNA replication which. Stage Stage 100 Stap Y Temperature 0 60 2 Time min a.
Sometimes called molecular photocopying the polymerase chain reaction PCR is a fast and inexpensive technique used to amplify - copy - small segments of DNA. Describe what happens to the. Explore the three steps of this revolutionary process.
Each of these polymerase chain reaction steps is. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Taq polymerase hooks new bases to the primer extending a new complementary piece of DNA.
This occurs when one or both allelic copies were not amplified during the polymerase chain reaction. Polymerase chain reaction PCR a technique used to make numerous copies of a specific segment of DNA quickly and accurately. The result is a huge number of copies of the specific DNA segment produced in a relatively short period of time.
The graph below shows how the temperature of the DNA in a reaction tube is changed during one cycle of the polymerase chain reaction PCR. These steps are repeated between 20 and 35 times to synthesize the correct quantity of the DNA of interest. It is repeated a specified number of times.
Because DNA polymerase can add a nucleotide only onto a preexisting 3-OH group it needs a primer to which it can add the first. The polymerase chain reaction PCR is a basic molecular technique used for amplifying target sequences from a DNA template in an exponential manner. DNA denaturation primer annealing and extension.
The new fragments of DNA that are made during PCR also serve as templates to which the DNA polymerase enzyme can attach and start making DNA. Like the nuclear chain reaction the polymerase chain reaction is an exponential. PCR has made it possible to generate millions of copies of.
-Describe what natural cellular process PCR mimics-List the 5 chemical components of a PCR reaction and describe their roles-List the functions of the 3 temperature cycles which are repeated during a PCR reaction-Describe the process of observing results and interpreting results of an experiment-Explain both the strengths and weaknesses of PCR. The first stage of this process occurs when the DNA is heated to produce two single strands that are separated. It is the creation of thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence.
Polymerase chain reaction PCR APBIO. PCR is based on three simple steps required for any DNA synthesis reaction. A polymerase chain reaction or PCR consists of three steps.
Polymerase chain reaction PCR. PCR or Polymerase Chain Reaction is a technique used in molecular biology to create several copies of a certain DNA segment. There are various types of DNA polymerases each of which has a specific function.
The final PCR step is when the DNA polymerase enzyme ie. IST1 EU IST1P LO IST1P1 EK A technique used to amplify or make many copies of a specific target region of DNA. The polymerase chain reaction enables investigators to obtain the large quantities of DNA that are required for various experiments and procedures in molecular biology forensic analysis evolutionary biology and medical diagnostics.


0 Response to "Describe What Happens During a Polymerase Chain Reaction"
Post a Comment